|
||||||||
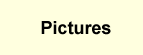 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Global Gene Expression Profiling in Neonatal Rat Myocardium in Response to the Anti-diabetic Agent Rosiglitazone | ||
|
Rosiglitazone is an anti-diabetic agent and a
high-affinity
ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
(PPAR gamma), which functions as a central regulator of
adipogenesis and lipid metabolism. Studies have shown that
rosiglitazone enhances insulin-mediated glucose uptake at the
whole-body level. However, the fact that the results of
several research studies and meta-analyses examining the
relationship between rosiglitazone and cardiovascular death
have so far been conflicting means that the safety of the drug
is yet to be determined. The work presented here is the first
step toward discovering the molecular events that lead to
association of rosiglitazone and the increased risk of heart
failure. To this end, we have employed Illumina's BeadArray
technology to examine the time course gene expression of
ventricular myocytes in neonatal rats under the treatment of
the drug and identified the differentially expressed genes and
relevant over-expressed biological processes and pathways.
| ||
| • Other Abstracts • | ||